Outcomes
Integrated Care Platform
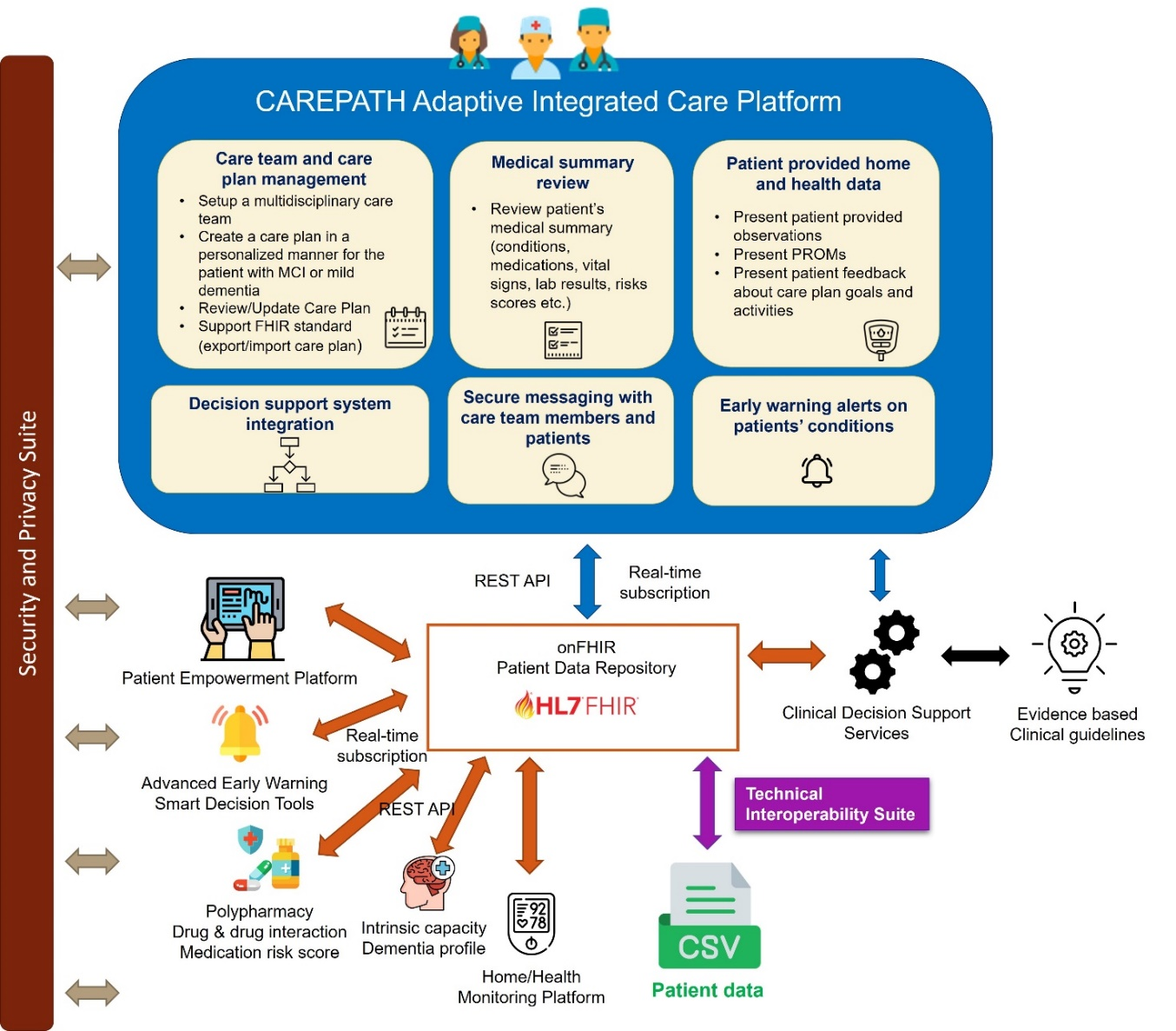
Integrated Care Platform jointly addresses multimorbidity, dementia and diminished intrinsic capacity and optimally manages healthcare interventions for its users, leading to a high degree of self-management of patients and significant support for the informal and formal caregivers (healthcare providers). As a new care pathway and healthcare model for the management of multimorbid elderly patients, this approach brings together:
An Adaptive Integrated Care Platform (AICP) for multidisciplinary care teams, with Clinical Decision Support Systems (CDSS) (based on Computer Interpretable Guidelines), to adapt the Care Plan of the patient based on his most recent health and wellbeing parameters and multimorbities as well as dementia profile and intrinsic capacity.
AICP is a Web-based system that enables the creation and execution of personalized care plans for multimorbid patients with mild cognitive impairment or mild dementia with the help of Clinical Decision Support Modules running in the background. It enables long-term and continuous coordination of patient-centred care activities by a multidisciplinary care team composed of health professionals, social care workers and homecare providers, and by the patients and their informal care givers, including family members. AICP acts as the direct interface to care team members, for defining, updating, reconciling, and sharing care plans. It also utilizes clinical decision support modules supporting these operations based on international clinical guidelines, receiving patient data from local Electronic Health Record systems, Patient Empowerment Platform, and Home/Health Monitoring Platform, and providing a dashboard for care team members to see basic medical history of the patient along with the care plan lifecycle history.
The Clinical Decision Support (CDS) services provide intelligent suggestions from clinical guidelines. AICP is integrated with the CDS services through the FHIR repository to present these suggestions to the healthcare professionals.
CDS services are implemented and integrated with AICP for the following clinical guidelines:- Mild Cognitive Impairment (MCI) & Mild dementia
- Sarcopenia & frailty
- Hypertension
- Diabetes
- Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD)
- Coronary artery disease (CAD)
- Heart failure
- Stroke
- Chronic kidney disease (CKD)
- Nutrition & hydration
- Physical exercise
- Caregiver support
- Commonly used drugs
A Health and Home monitoring platform (H/HMP), with intelligent data analytics tools to estimate dementia profiles and intrinsic capacity of patients.
Home/Health Monitoring Platform (H/HMP) is the component responsible for collecting, filtering and integrating data coming from health sensors and home automation devices, The H/HMP queries the Patient Data Store, consolidates the patients’ information (EHR data, information coming from PEP, data coming from external information systems, etc.) thus obtained with sensor data, and stores results in the H/HMP Data Store. Next, various other modules in the system will interact with the H/HMP for their own processing purposes, specifically, but not only, the FHIR based Common Data Model (which stores in the FHIR Repositories) and the Early Warning Services.
H/HMP technologies follow a general architecture that consists of four components:- Sensors on devices enabled by wireless communications to measure physiological parameters. Sensors can connect back to a central database by Wi-Fi or cellular communication protocols depending on the manufacturer, or on data stores (clouds) at the manufacturer premise.
- Local data storage at patients’ site that interfaces between sensors and other centralized data repository and/or healthcare providers.
- Centralized repository to store data sent from sensors, local data storage, diagnostic applications, and/or healthcare providers.
- Diagnostic application software that develops treatment recommendations and intervention alerts based on the analysis of collected data.
A framework for Polypharmacy Management
More than half of all patients older than 65 years take more than 5 prescription drugs 90% of these patients additionally take more than one freely available drug, 50% take 2 to 4 of these preparations High risk for drug-drug interactions and other adverse events Potentially inappropriate prescribing (PIP) is a problem. Further worsened due to incomplete case histories, low patient compliance or other inaccuracies and missing knowledge. There are criteria/guidelines for evaluating prescriptions so called screening tools for identifying polypharmacy. T hese guidelines are mainly paper based and not computerized, so they have to be applied manually by a medical professional. In the special case of elderly patients’ development started with Mark Beers’ list of inappropriate medications (1991) followed by other evidence-based rules.
The criteria try to minimize inappropriate prescribing. Published in 2008, updated in 2014 with a total of 114 rule statements. In CAREPATH is build on previous prototypes and customize the STOPP/START rules as computerized tool to identify in appropriate prescriptions of patients. The CAREPATH polypharmacy tool provides a REST API interface invoked by AICP providing patient data such as age and gender, conditions as ICD numbers and a list of medicaments including the ATC codes of each medicament. The polypharmacy tool walks through all rules and check if any of them will fire. A firing rule will generate textual recommendations that will be compiled together and sent back to the AICP as FHIR CDS cards.Early Warning Services (EWS)
The Early Warning Services (EWS) incorporate an internal rule engine as well as advanced technologies such as artificial intelligence and machine learning, to provide dynamic early warning about the development of the condition as well as the suitability of the treatment, namely:- effectiveness of medication and detection of side-effects;
- development of a risk stratification model and definition of how the risk categories will be monitored by the various tools.
- continuous monitoring of trajectories of intrinsic capacity and dementia profile by integrating patient data collected both passively and actively from home/health monitoring platform.
A Patient Empowerment Platform (PEP)
Patient Empowerment Platform (PEP) is the main interface of patients and their informal care givers. Through PEP they can review their care plan, display daily activities including exercises, diet plan, medication intake, home measurements, appointments, and referrals, provide feedback about care plan goals and activities, report symptoms and patient reported outcome measures (PROMs), access educational materials, exchange messages with care team members, and retrieve notifications and reminders.
PEP is composed of three components:- PEP Mobile UI: deployed on the patients tablet
- PEP Web UI: provided to informal caregivers
- PEP Engine: coordinates the internal business logic of the functionalities provided by PEP
The Advanced Early Warning Smart Decision Tools gets inputs from PEP, H/HMP, Interoperability Framework, CDSS and outputs results to the Adaptive Care Planner to adapt the care pathway based on the current dementia profile of the patient.
Technical Validation and Usability (TVU) study and Clinical Investigations (CI)
Involving over 45 users and Clinical Investigation (CI) involving
over 200 patients that will be conducted in four European countries (Spain, Romania, Germany and UK).
Technical Validation and Usability (TVU) study will be performed to capture and fix usability issues before the clinical investigation starts, and to
evaluate usability, users’ experience and safety of the CAREPATH ICT platform, by collecting feedback from stakeholders in the four pilot sites
(SKB - Germany, UHCW - UK, SESCAM - Spain and CITST - Romania) across Europe.
TVU will involve 45 target end users (16 patients with MCI or mild dementia with their informal caregivers and 16 healthcare professionals
from various disciplines), and will last 3 months (90 days).
Clinical Investigation (CI) study, following TVU, will be a two-year campaign, to provide initial and indicative clinical validation of the implemented platform,
involving 200 patients 100 users to pilot the CAREPATH platform and 100 patients as reference cases). It will be coordinated in the four European pilot sites
(SKB, UHCW, SESCAM, CITST) with diverse health and social care systems, ICT landscape/digital maturity of healthcare provision and dementia national programs,
which will allow for strengthening the evidence base on health outcomes and efficiency gains.
Dementia / Multimorbidity Guidelines
To be conceived for best healthcare delivery, analyses will be conducted in finding the literature review and developing the holistic CAREPATH best practice guideline. This will take place in three stages. Firstly, the task will compose a supra pilot site guideline, which will be identified as a set of evidence-based guidelines for the diseases selected for CAREPATH investigational pilot studies eligibility criteria. Secondly, a gap analysis will be performed identifying aspects of dementia, intrinsic capacity, and multimorbidities identified in the literature review, but not covered by selected set of clinical guidelines addressing the needs of individual diseases. Evidence based practice, about those aspects, will be incorporated within the CAREPATH guideline, by parametrizing several decision points in terms of specific elements in dementia, intrinsic capacity and multimorbidity. In addition, this stage will identify and reconcile potential conflicts amongst guidelines, including conflicting goals, patient objectives as well as conflicting medications. The third phase will review the CAREPATH guideline and will incorporate customisations for local practice at the pilot sites. The task will be performed with involvement by clinicians at the pilot sites, and the clinical reference group will review the final guideline. CAREPATH will consider the best available evidence that will be provided by the literature review, to design a patient-centered guideline, aiming to alleviate the pressures to the healthcare system, as well as to increase the quality of patients (as defined by the project).
Health Economics Impact Assessment
For healthcare cost effectiveness and care provision equalities. The incremental cost-effectiveness and the incremental cost-utility ratio would allow revealing the incremental cost (or the potential savings) per unit of benefit of switching from usual care to CAREPATH-an integrated patient-centred approach- in multimorbid elderly patients with dementia, and therefore, to determinate whether the CAREPARTH approach would be considered as a cost-effective alternative.
 This project has received funding from the European Union’s
Horizon 2020 research and innovation programme under grant
agreement No 945169
This project has received funding from the European Union’s
Horizon 2020 research and innovation programme under grant
agreement No 945169